Soft Tissue Grafting in Stamford
Gum Grafting
If you have been referred for a gum graft, your dentist may be concerned about one of the following:
- Recession
- Mucogingival defect
- Restorative margins
- Aesthetics
- Tooth sensitivity
- Orthodontic movement
- High frenum
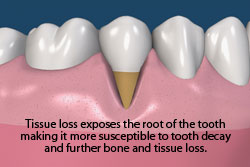
Gum recession is the migration of tissue down the tooth surface and often occurs after bone loss. Gum recession can result in a loss of attached keratinized tissue (mucogingival defect), tooth sensitivity, root decay, an unaesthetic smile or appearance, and root gouging.
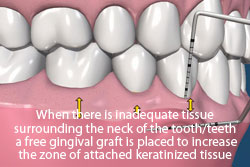
Keratinized tissue is the strong, pink, non-movable tissue that sits around the neck of the tooth protecting the tooth and the underlying bone from bacterial penetration and trauma. The mucosa, the movable weaker tissue, sits below attached keratinized tissue and covers the bone.
A gum graft is a surgical technique which is used to enhance and/or restore the gingival shape and form back to a healthy state. There are two main types of gum grafts: gingival and connective tissue. The techniques may vary from periodontist to periodontist, but both types of grafts are designed to prevent gum recession.
Ginigval
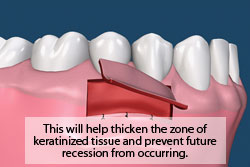
A gingival graft increases the zone of keratinized tissue. In this procedure, the recipient site is prepared by surgically resecting and repositioning the mucosa away from the affected teeth. A small piece of tissue (donor tissue) is then removed from the roof of the mouth and transplanted over the recipient site. Both the recipient site and the donor site are sutured and a packing is placed over both sites to increase patient comfort.
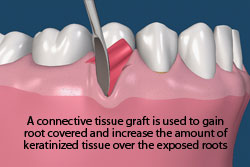
Connective Tissue Graft
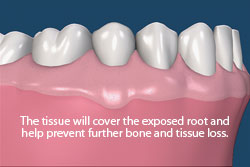
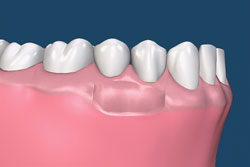
A connective tissue graft is designed to increase the zone of keratinized tissue as well as to achieve root coverage and decrease root sensitivity. This procedure involves reflecting tissue away from the affected teeth (recipient site). A small piece of tissue from inside the palate (donor site) is removed and is then transplanted into the recipient site. In some cases Allograft, which is tissue from another individual, is used as the donor tissue. The connective tissue graft is traditionally more comfortable for patients because it does not leave an exposed area on the palate.